Getting Started with Database
Database focuses on a particular academic discipline or specific material types. It is very useful on academic researches as it stores a lot of digitalized articles. Here we will instruct you how to use a database! 【中文說明請見此文章:資料庫指引】
1. Database Guidelines
![]() By material type
By material type
- Electronic-books: Have the access to the information anytime and anywhere.
- Journal articles: Find the latest research results here for referencing.
- Dissertation and theses: Find the sources that are relevant to your research papers and make reference to a research methodology adopted in another thesis.
- Newspapers: Provides current affairs on a daily basis and you may trace the development of social issues.
- Encyclopedia: Text is revised by specialists and it covers authoritative summary information about a variety of topic.
- Patent: the key technology of new inventions is seldom shown in public. Therefore, patent database provides important information for studying practice technology.
- Standards: Normative documents or specifications that are developed by the organization and this serves as a valuable referencing for engineering field.
- Protocol: Content of experiments are proven and they assist researchers to design and implement the experiments.
- Overseas Industry reports: Provide industrial researches and overall development of a specific country, type of industries and particular companies.
- Impact factor: Number of cited and the ranking of academic journals.
- Language learning: Utilizes the NTUL collection and e-learning program is provided if you are interested in learning English, Japanese , French, German and other languages.
- National Competitiveness: Data is published by authority organization e.g. WEF.
- National basic information: Indispensable information in doing globalization researches and regional studies.
- Magazines: Includes digitalized magazines such as The Economist, Harvard Business Review, Time and Fortune etc.
- Exporting charts and graphs: A minority of databases offer a function of exporting the graphs to PowerPoint.
–
![]() By subjects
By subjects
- General subjects: “Web of Science”, “SCOPUS” etc.
- Biological, Biomedical and Agronomy: Biological “BIOSIS Previews” ; Biomedical and Medicine “PubMed” ; Agronomy “CAB Abstracts”, “AGRICOLA” etc.
- Science and Technology: Physics “IOPScience” ; Chemistry “Reaxys”, “ACS”, “RSC” ; Psychology “PsycINFO” ; Electrical Engineering and Computer Science “IEEE” etc.
- Humanities and Social Sciences: Chinese ancient books “中國基本古籍庫”, “全四庫” ; Languages and literatures “MLA”, “HUSO” ; Business administration and Finance “ABI/Inform”, “BSP”, “TEJ” ; Law “LexisNexis” etc.
–
2. How to learn in using databases?
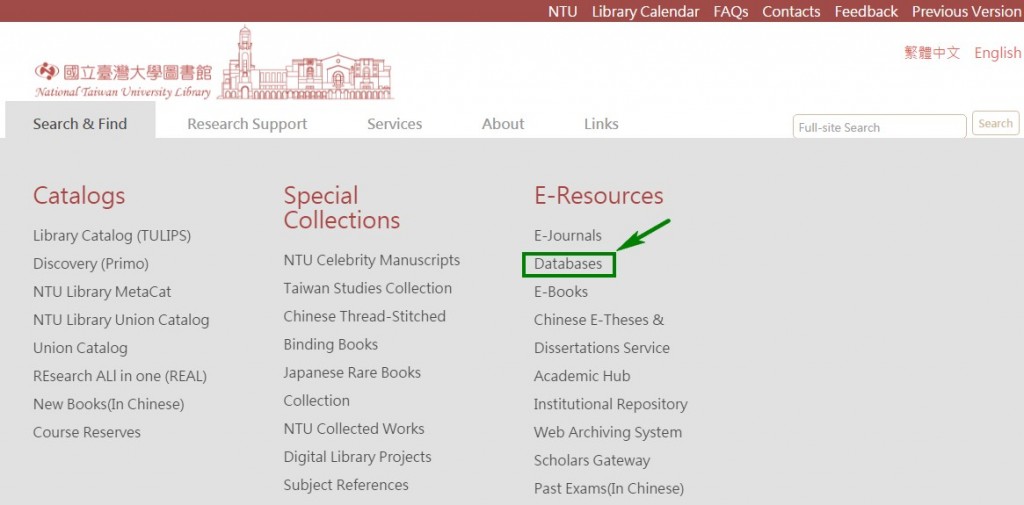
Step1: Enter Library Homepage and select Search & Find → E-Resources→ Databases
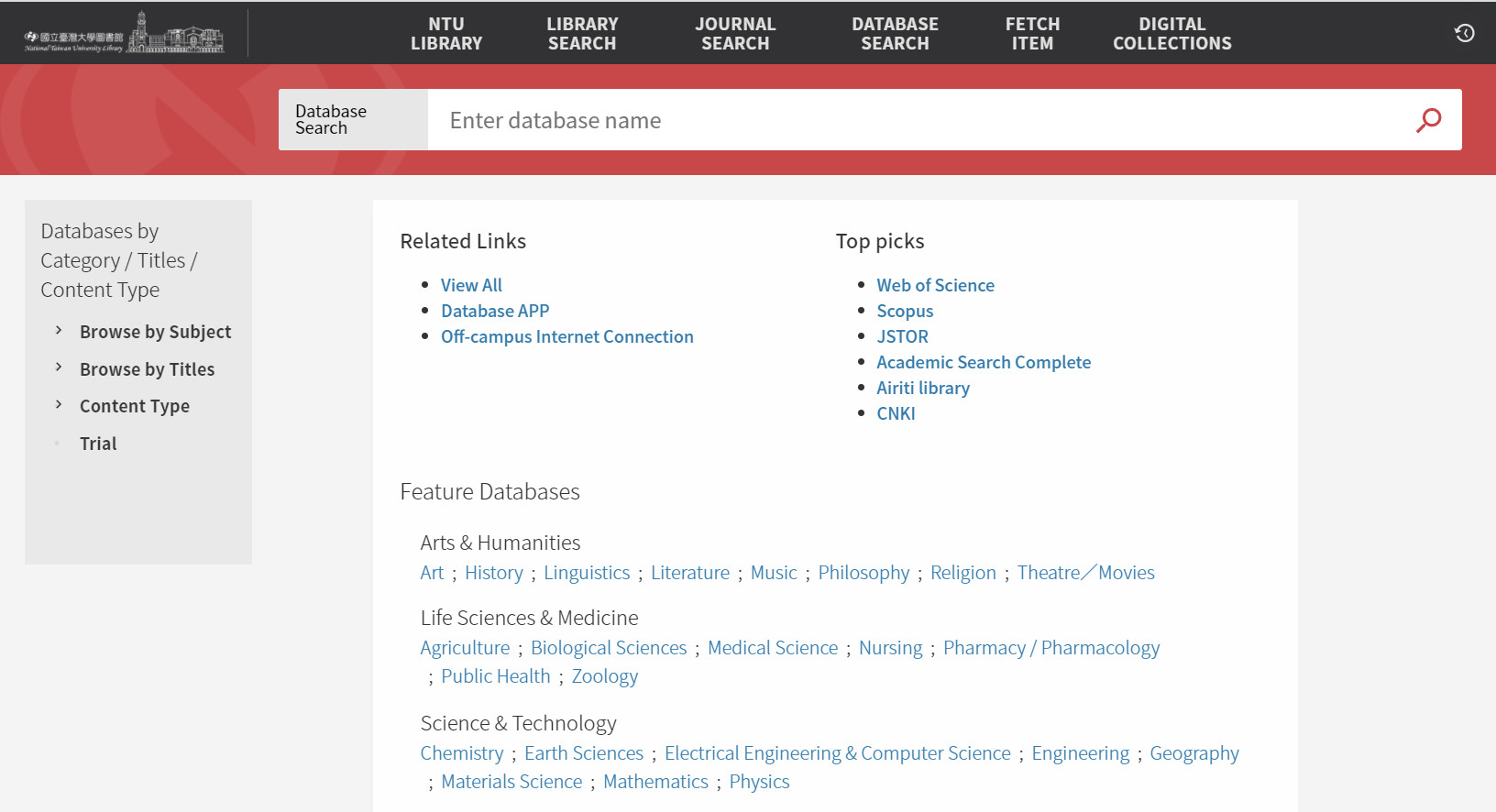
Step2: Browse by subject, titles, content type, or use keyword searching to find a relevant database.
Step3: If NTU students and staff want to use the database outside the campus, please set up VPN.
4. How to organize references?
You can use bibliographical management software! It allows library users to create a library of references. Also, it assists you to organize your bibliographic references and retrieve citations. There is a lot of bibliographical management software and NTUL has subscribed “EndNote”. You may use free bibliographical management software, e.g. Mendeley.
–
![]() If you have other in-depth questions, please e-mail to tul@ntu.edu.tw .
If you have other in-depth questions, please e-mail to tul@ntu.edu.tw .
![]() We are looking forward to helping you in using library services.
We are looking forward to helping you in using library services.
Written by YoYo Cheung, Intern from The University of Hong Kong.
特別感謝香港大學資訊管理系實習生張楚瑤同學翻譯及撰寫此篇英文文章!
Revised by Chih Lo Chen 2015/4/8, 2017/1/9, 2018/11/20, 2020/11/9